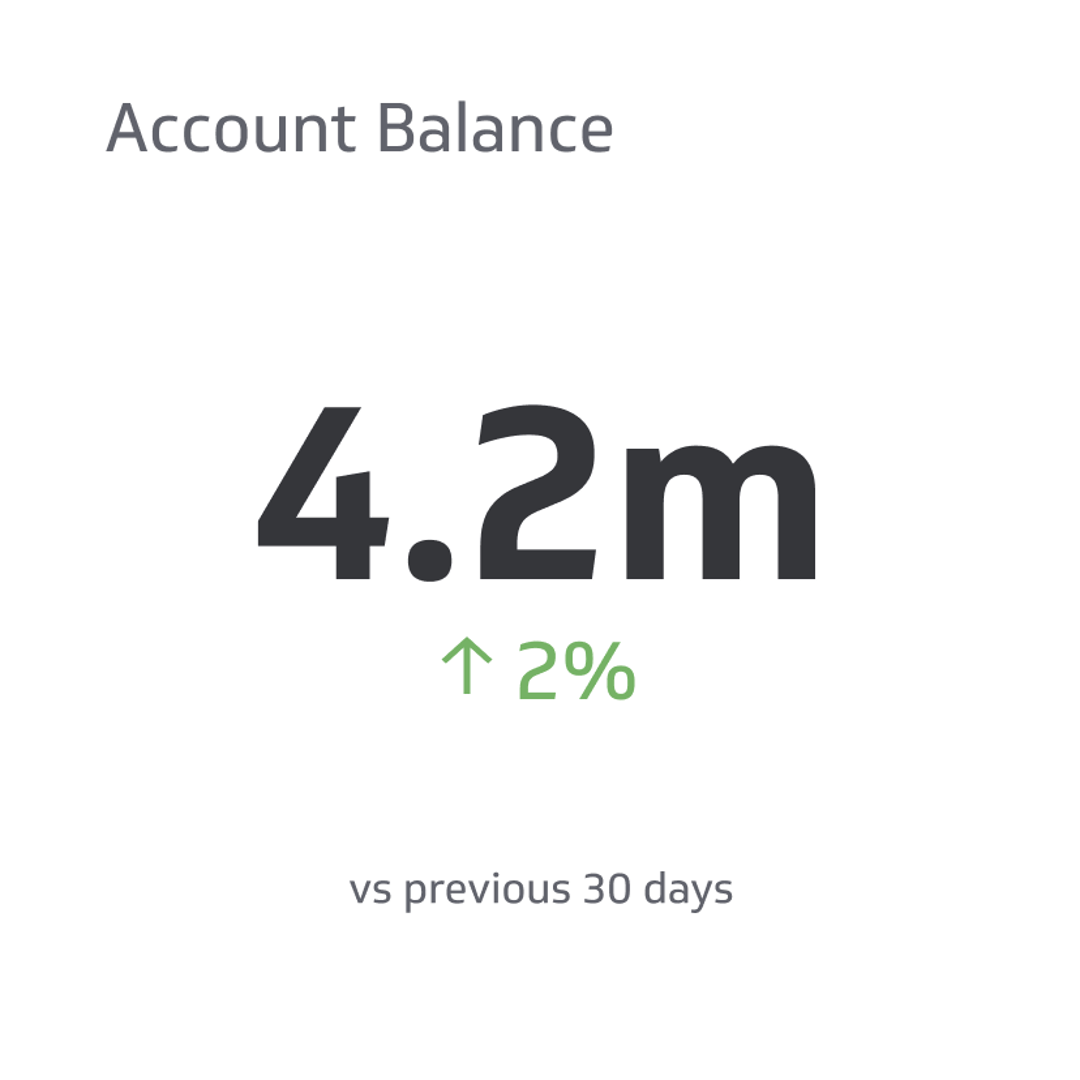
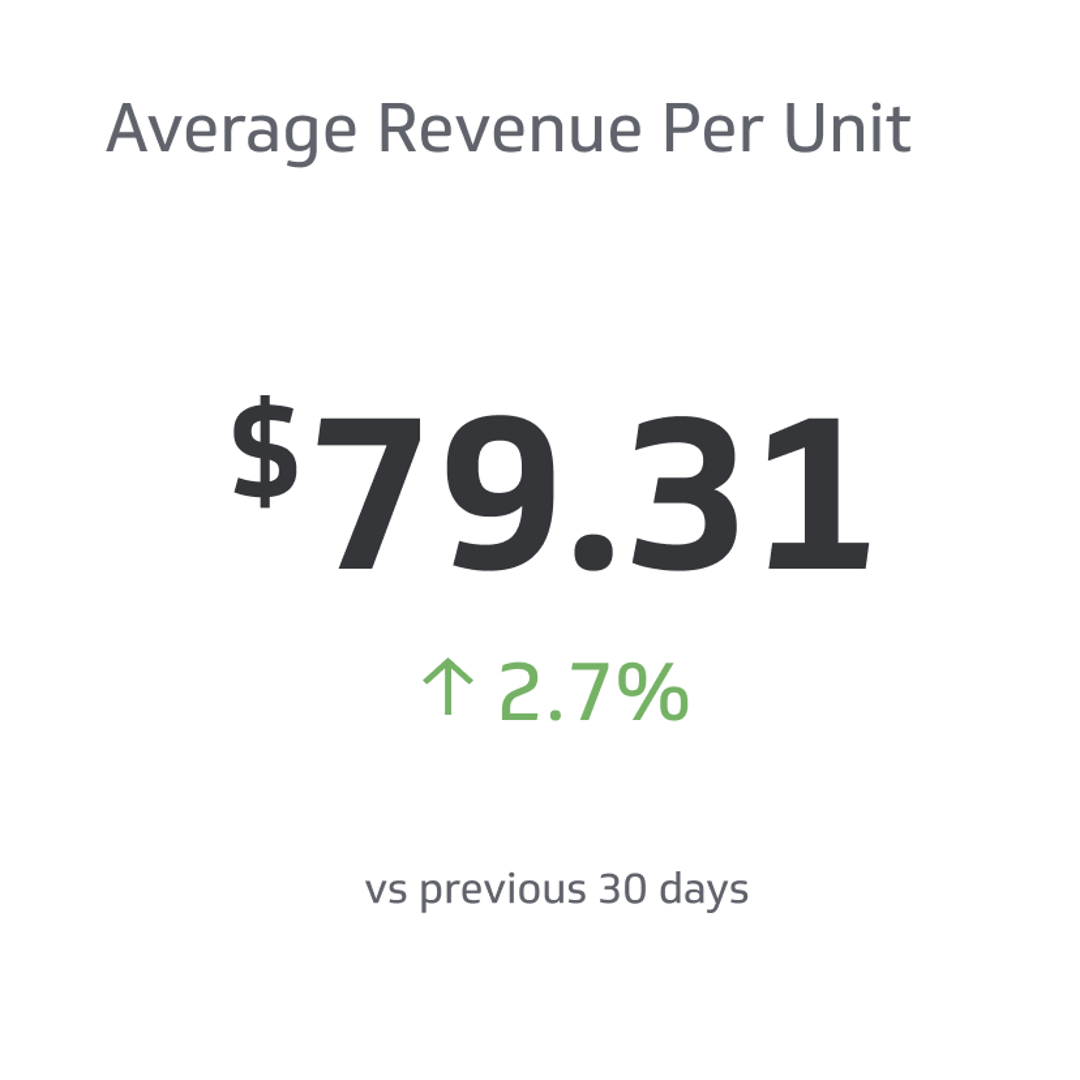
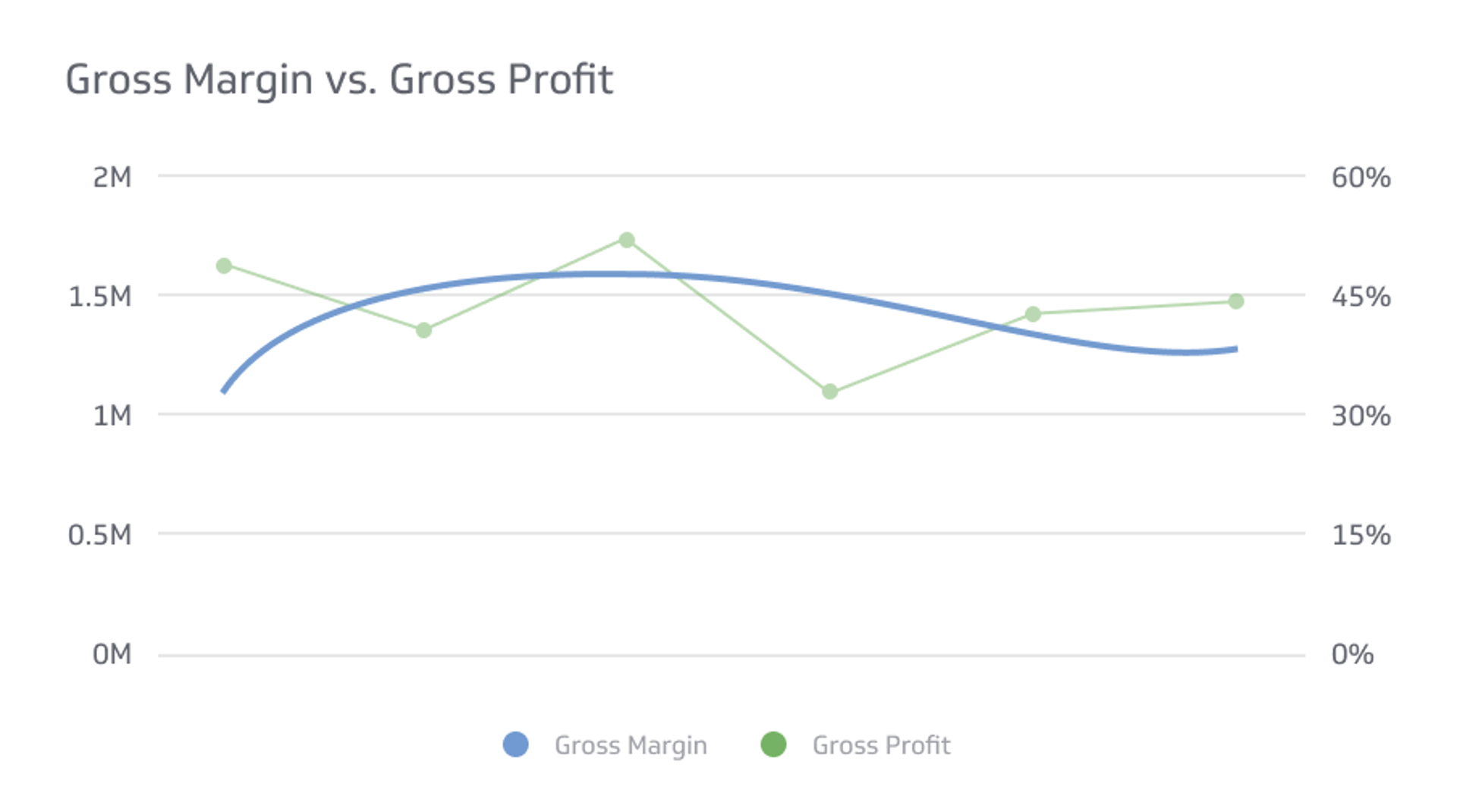
Payroll Expenses
Payroll expenses represent the costs associated with paying employees for their work, reflecting the gross pay and any relevant withholdings and payroll taxes.
Track all your Financial KPIs in one place
Sign up for free and start making decisions for your business with confidence.
If you are running a business, understanding payroll expenses is essential for keeping your finances in order. Payroll is more than just the wages and salaries of your employees. It encompasses taxes, benefits, deductions, overtime pay, Social Security and Medicare contributions, and more.
Understanding these payroll components can help you stay compliant with the law while maximizing profits for yourself and your company. In this blog post, we will explore payroll expenses so you can ensure your finances are managed appropriately.
Payroll Expenses
Payroll expenses represent the costs associated with paying employees for their work, reflecting the gross pay and any relevant withholdings and payroll taxes.
Data collection, analysis, and maintenance are necessary for businesses to manage their payroll expenses effectively. The resulting costs can vary regularly based on various factors, making ongoing monitoring and cost analysis a crucial component of any organization's financial strategy.
Ensuring the accuracy of these expenses is vital for regulatory compliance, strategic planning, and overall business success.
Payroll Expenses for Employers
There are two types of costs to consider. Firstly, the subtraction of employee salaries includes contributions to benefits such as insurance, retirement funds, and any other deductions agreed upon in the employment contract.
Secondly, the employer's payroll taxes and obligations include social security, Medicare, and unemployment taxes.
Withholding Taxes
Withholding taxes refer to the amount of money you withhold from your employee's paycheck to pay for their taxes. The exact amount that needs to be withheld can be determined by the W4-form filled out by your employee.
The taxes to be withheld may include the following:
- State Income Tax (SIT)
- FICA (Medicare and Social Security)
- Federal Income Taxes (FIT)
Unemployment Tax Withholdings
Unemployment tax withholdings can provide workers with crucial income as they search for new job opportunities. The Federal Unemployment Tax Act and State Unemployment Tax Act offer temporary financial assistance for those who find themselves unemployed.
The first $7,000 of a worker's gross income is taxed at the current employer's FUTA tax rate of 6%. However, if a state unemployment tax applies to wages, the employer may use a 5.4% FUTA credit to lower the tax to 0.6%.
The specific combined federal and state unemployment taxes vary depending on the unemployment program in each state.
Benefits Withholdings
As an employer, you likely understand the importance of offering employee benefits. It's a strategic move that can lead to a happier workforce, higher employee retention, and overall success for your business. However, administering these benefits can be complicated, especially regarding withholdings.
Benefits withholding refers to deducting an employee's share of the benefit plan from their gross compensation. Depending on your arrangement with your employees, you may cover a portion, or all of the benefits cost.
These benefits can range from insurance for workers' compensation and health protection to 401(k)s or other retirement plans with life insurance.
Payroll Expenses for Contractors
One of the significant differences between hiring contractors and employees is their tax responsibilities. As employers, we hold the responsibility for withholding taxes for our employees.
When hiring contractors, they are solely responsible for their FICA and benefit plans. This makes things easier for employers when navigating tax matters related to employees versus contractors.
When we pay contractors their gross compensation, they handle the complexities of tax withholdings, making it a seamless transaction.
What Is the Difference Between Salary Expense and Payroll Expense?
While the terms seem interchangeable, they refer to two different aspects of an employee's compensation.
Salary expense refers to the amount paid to an employee as salary or wages. In contrast, payroll expense encompasses a broader range of costs related to paying employees, such as payroll taxes and benefits.
Calculating an employee's net salary involves accounting for taxes and other deductions, while payroll refers more broadly to the payment method.
How To Calculate Payroll Expenses
Calculating payroll expenses is an essential and often time-consuming process for any business. To ensure accuracy, you must gather data such as employee hours, rates of pay, and any federal and state tax withholdings.
Once you have this information, you can make the necessary calculations. Pay close attention to detail, as even the slightest mistake can have significant consequences.
After processing the payroll, you must pay your employees and submit withheld funds to third parties according to the appropriate deadlines.
Employees Should Complete the W-4 Form
All new employees must submit their Form W-4 upon starting a new job. The W-4 determines how much of an employee's paycheck will go toward taxes. Employees can ensure they're not withholding too much or too little from their paychecks by accurately listing the appropriate allowances.
In addition, for those with multiple jobs or working spouses, the W-4 can be a valuable tool for navigating complicated tax situations.
Determine Gross Pay
Determining gross pay is a crucial step in payroll processing. It is the starting point that sets the foundation for accurate payment calculations. The formula for calculating gross pay varies depending on the payment frequency - hourly, bi-weekly, or monthly.
Keep track of the number of hours worked throughout the relevant time to determine the gross pay for hourly workers. Gross pay for salaried workers is commonly calculated by dividing their annual income by the number of pay periods in the year.
Calculate Net Pay
To calculate net pay, you must gather all the relevant data, including your gross pay, federal and state taxes, social security and Medicare deductions, and any other withholdings.
Once you have all the information, you can use a net pay calculator or manually compute it to get an accurate figure.
Submit Payroll Tax Deposits
As a business owner, you must keep current with your tax obligations. Submitting your payroll tax deposits is one of these responsibilities. The frequency of these deposits depends on the dollar amount.
Regarding payroll tax deposits, you need to include FICA and FUTA taxes and federal, state, and local income taxes. With online tax deposit payments, you can simplify this process while ensuring you submit your tax returns on time.
Complete Payroll Tax Forms
To make things simple, there are four standard payroll tax forms available. Form 941 informs the IRS of the federal income taxes and FICA taxes paid each quarter. Form 940 is the yearly federal unemployment (FUTA) tax return.
Form W-3 discloses each employee's total earnings and tax deductions, which must be submitted annually to the Social Security Administration. And finally, the money paid to independent contractors using 1099 forms should also be reported.
Report Pay Amounts to Workers
As a responsible business owner, you should accurately and timely report all payment amounts. This includes providing a 1099 to any contractor who earns $600 or more from your company in a given year.
Even if a contractor earns less than $600, their earnings are still taxable and must be recorded on their tax return. In contrast, employees receive a W-2 that details their gross salary and annual tax withholdings.
Keep Records on File
Under the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA), businesses must keep employee time and pay records on file for at least two years. This is crucial to ensure compliance with federal and state regulations and avoid potential legal or financial consequences.
Furthermore, keeping records up-to-date helps businesses make informed decisions about staffing and budgeting and stay on top of any tax regulations or employee withholdings changes.
Conclusion
With this knowledge of how payroll expenses are calculated, organizations can comply with tax laws and best practices and inform their employees about their pay. Payroll expenses are an essential part of any organization because they represent a cost that is often overlooked but significant for managing employee morale and motivation.
As a result, it's important to closely review your payroll expenses and ensure you're accurately tracking deductions and taxes so all employee payments are accurate.
Related Metrics & KPIs