Gross Margin vs. Gross Profit
Gross margin and gross profit are two financial metrics that help provide insight into a company's profitability and cost management.
Track all your Financial KPIs in one place
Sign up for free and start making decisions for your business with confidence.
Gross margin and gross profit are two financial metrics that help provide insight into a company's profitability and cost management. Gross profit is the revenue a company has left after subtracting the cost of goods sold (COGS), while gross margin is the percentage of revenue that represents gross profit.
These metrics are important for investors and analysts because they provide a snapshot of the company's core operations and profitability. In addition to understanding how to calculate and interpret these metrics, it's important to consider other factors that affect a company's financial health. These include but are not limited to operating expenses, taxes, and interest payments.
Statistics on Gross Margin and Gross Profit
According to a report by McKinsey & Company, gross margin is a key driver of profitability in most industries. The report found that companies with higher gross margins also tend to have higher profit margins. For example, in the technology industry, companies with a gross margin of 60% or higher had a median profit margin of 26%, while those with a gross margin of 40% or lower had a median profit margin of only 4%.
Another report by Deloitte found that gross margin is particularly important for retailers. The report found that retailers with a gross margin of 40% or higher tend to have better financial performance than those with lower gross margins. Additionally, retailers that increased their gross margin by 1% saw an average increase in earnings before interest and taxes (EBIT) of 12%.
These statistics highlight the importance of understanding gross margin and gross profit to evaluate a company's financial health and make informed investment decisions. By calculating and analyzing these metrics, investors can gain valuable insights into a company's profitability and cost management, which can help them identify potential risks and opportunities.
What is Gross Profit?
Gross profit is a company's total revenue from selling its products or services minus the cost of goods sold (COGS). The cost of goods sold includes the direct expenses associated with producing or acquiring the products or services that the company sells. Examples of COGS include raw materials, labor costs, and manufacturing overhead.
To calculate gross profit, subtract the COGS from the total revenue:
- Gross profit = Total Revenue - Cost of Goods Sold
Gross profit measures a company's profitability before factoring in other expenses, such as operating expenses, taxes, and interest payments.
What is Gross Margin?
Gross margin is a percentage that represents the portion of each dollar of revenue that remains after subtracting the COGS. The formula is
- Gross Margin = (Gross Profit / Total Revenue) x 100%
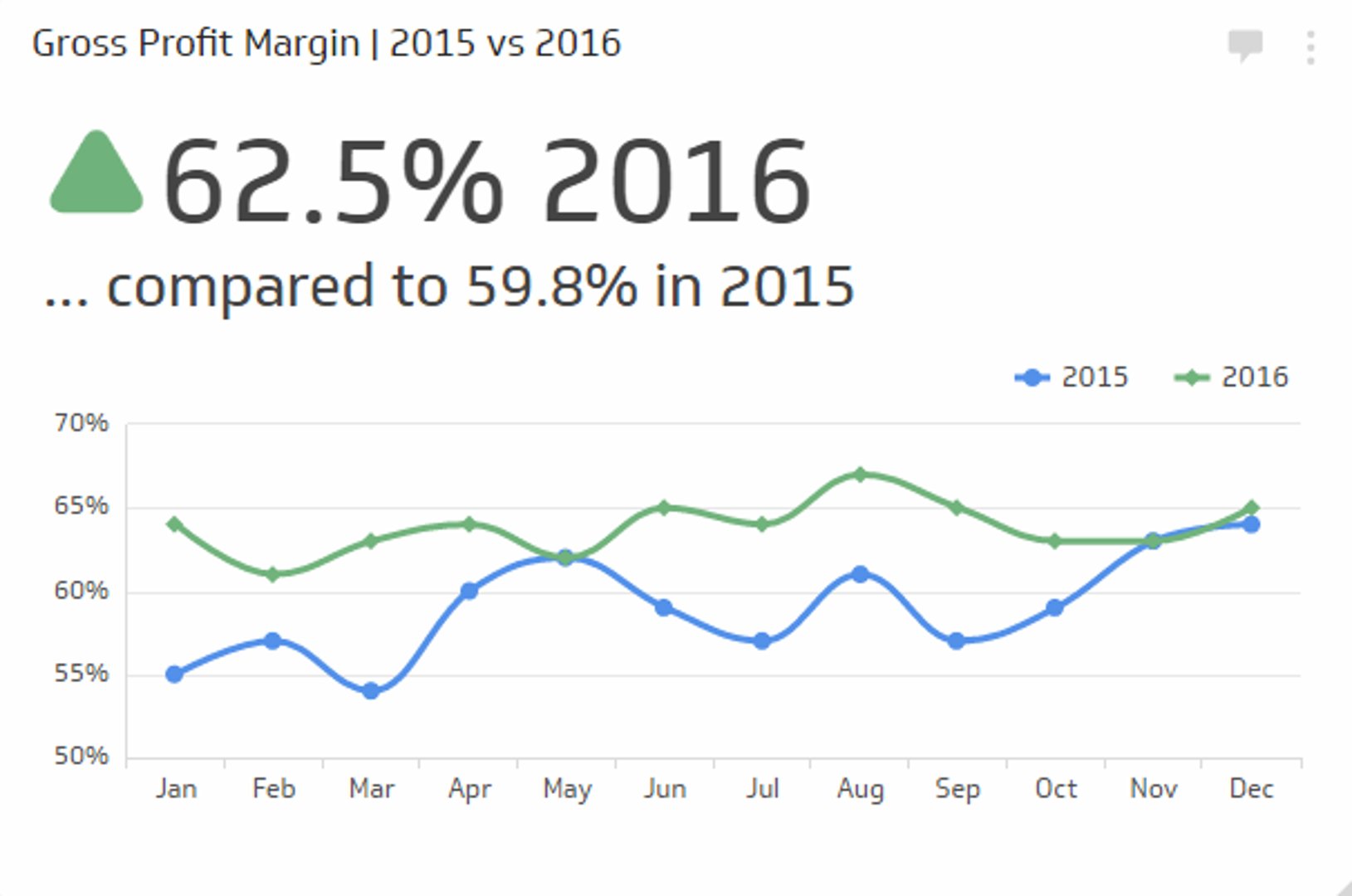
Gross margin provides insight into a company's profitability as a percentage of its revenue. A higher gross margin means a company can profit more from each sales dollar.
Differences between Gross Profit and Gross Margin
While gross profit and gross margin are measures of a company's profitability, they reveal different information about its financial health. Gross profit is an absolute dollar amount, while gross margin is a percentage.
Gross profit is a measure of the profitability of a company's core operations, excluding other expenses such as operating expenses, taxes, and interest payments. It provides insight into how much money a company has left over after paying for the direct expenses of producing or acquiring its products or services.
Gross margin, on the other hand, measures the profitability of a company's core operations as a percentage of its total revenue. It provides insight into how much profit a company can generate from each sales dollar.
How to Use Gross Margin and Gross Profit
Gross margin and gross profit can be used to evaluate a company's financial health and performance over time. Investors and analysts often use these metrics to compare companies within the same industry and to identify trends in a company's profitability.
A company with a high gross profit and gross margin is generally considered more profitable and financially stable than one with a lower gross profit and gross margin. However, it's important to note that gross margin and gross profit do not provide a complete picture of a company's financial health. Other factors, such as operating expenses, taxes, and interest payments, can also impact a company's profitability and financial performance.
Importance of Gross Margin and Gross Profit
Gross margin and gross profit are important financial metrics because they help companies and investors understand the profitability of a company's core operations. They also provide insight into a company's ability to manage its costs and generate revenue.
By comparing a company's gross profit and gross margin to its competitors, investors can better understand how it performs relative to others in the same industry. For example, a company with a higher gross margin than its competitors may be able to charge higher prices for its products or operate more efficiently than its competitors.
However, a company with a low gross margin or gross profit may be operating at a loss, which could be a red flag for investors. Companies may deliberately operate with a lower gross margin to gain market share or reduce prices to remain competitive.
Calculating Gross Margin and Gross Profit
To calculate gross profit, subtract the cost of goods sold from the total revenue. For example, if a company has total revenue of $500,000 and a cost of goods sold of $250,000, the gross profit would be:
- Gross profit = Total Revenue - Cost of Goods Sold
- Gross profit = $500,000 - $250,000
- Gross Profit = $250,000
To calculate gross margin, divide the gross profit by the total revenue. Then, multiply by 100 to express the result as a percentage. Using the same example as above, the gross margin would be:
- Gross Margin = (Gross Profit / Total Revenue) x 100%
- Gross Margin = ($250,000 / $500,000) x 100%
- Gross Margin = 50%
Interpreting Gross Margin and Gross Profit
A high gross profit and margin are considered positive indicators of a company's financial health. However, it would help if you considered other factors impacting a company's profitability, such as operating expenses, taxes, and interest payments. For example, a company with high operating expenses may have a lower net profit margin despite having a high gross profit and gross margin.
It's also important to compare gross profit and gross margin to industry benchmarks and to track changes over time. A company with a declining gross margin or gross profit may be experiencing increased competition or rising costs, which could negatively impact its profitability.
Factors That Impact Gross Margin and Gross Profit
Several factors can impact gross margin and gross profit. One of the most significant is the cost of goods sold (COGS). This includes costs associated with producing and delivering a product. This can include the cost of raw materials, labor, and shipping.
In addition to COGS, other factors that can impact gross margin and gross profit include pricing strategy, competition, and changes in consumer demand. For example, if a company reduces prices to gain market share, it may see a decrease in gross margin and gross profit.
It's also important to note that gross margin and gross profit vary widely between industries. For example, companies in the software industry typically have higher gross margins than those in the retail industry due to the lower cost of goods sold.
How Gross Margin and Gross Profit Relate to Net Profit
Gross profit is an important component of net profit, which is a company's total profit after all expenses have been deducted. Net profit is calculated by subtracting gross profit from operating expenses, taxes, and interest payments.
A company can have a high gross profit and margin but still have a low net profit if operating expenses or other costs are high. Conversely, a company with a low gross profit and gross margin can still have a high net profit if it can manage its expenses effectively.
Using Gross Margin and Gross Profit for Decision-Making
Companies often use gross margin and gross profit to make pricing, production, and marketing decisions. By analyzing gross margin and gross profit data, companies can identify areas where they can reduce costs, increase efficiency, or charge higher prices.
For example, if a company's gross margin is lower than its competitors, it may need to examine its production process to identify areas where it can reduce costs. Alternatively, if a company's gross margin is higher than its competitors, it may charge higher prices without sacrificing profitability.
FAQs
How does Gross Profit Differ from Net Profit?
Gross profit is the revenue a company has after the cost of goods sold (COGS) is deducted, while net profit is the total profit a company earns after all expenses incurred, including operating expenses, taxes, and interest payments.
Why is gross margin important?
Gross margin is important because it provides insight into a company's profitability and cost management. A high gross margin indicates that a company can generate more profit from its core operations, while a low gross margin may suggest that a company is facing challenges with pricing, competition, or cost management.
What factors can impact gross margin and gross profit?
Factors that can impact gross margin and gross profit include the cost of goods sold (COGS), pricing strategy, competition, and changes in consumer demand. In addition, gross margin and profit can vary widely between different industries.
How can gross margin and gross profit be used for decision-making?
Companies can use gross margin and gross profit to make pricing, production, and marketing decisions. By analyzing gross margin and gross profit data, companies can identify areas where they can reduce costs, increase efficiency, or charge higher prices.
Conclusion
Gross margin and gross profit are important financial metrics that help understand a company's profitability and ability to manage costs. By understanding how to calculate and interpret these metrics, investors can better understand a company's financial health and make informed investment decisions.
However, it would help to consider other factors that may impact a company's profitability and compare these metrics to industry benchmarks and historical trends. This will help you make a better decision.
Related Metrics & KPIs